Water preservation is a constant issue for India because the farming sector forms the essential foundation of its economy. The population growth combined with rising agricultural needs makes it vital to develop innovative water management solutions. A revolutionary water conservation technology called rubber dams can reshape India's irrigation system. Yooil Envirotech emerged as a pioneer company and transformative leader dedicated to building sustainable water resource management systems.
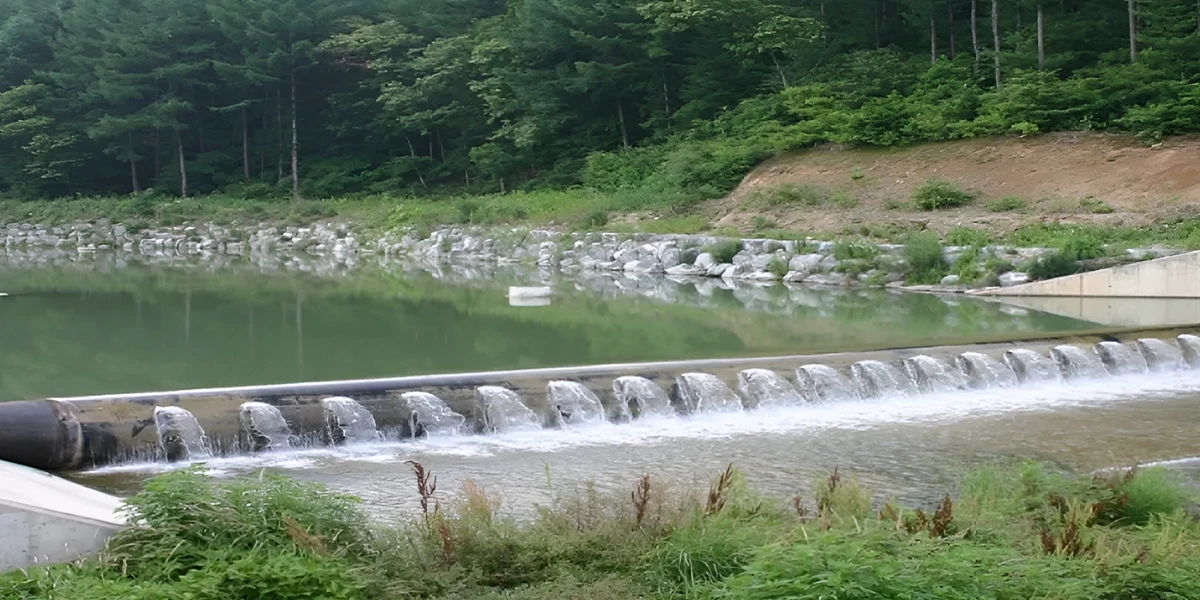
The rubber dam is a flexible inflatable barrier system that maintains water flow management while performing flood control and water storage. Traditional concrete-based reservoirs differ because rubber-made structures depend on high-strength viscoelastic fabric, which operators use to inflate or deflate the systems when required. The ability of a rubber dam in India to adapt to different water needs makes them suitable for operating in locations which need flexible water management systems.
There are different Rubber dam types, depending on their operation and installation needs:
Each type serves a unique purpose, making rubber dams versatile for water conservation, flood control, and irrigation management.
India’s farm sector depends on monsoon rain, yet unanticipated rainfall causes floods or droughts. The efficient rubber dam water storage technique permits the collection of excess rain for distribution during dry spells. The regular water supply protects farming from weather-dependent natural water supply systems.
Some key ways rubber dams contribute to agricultural water conservation include:
The rubber dam advantages as an alternative to traditional structures exist because of their substantial advantages:
Rubber dams present a perfect water conservation solution for agricultural areas which require water scarcity management in India.
Yooil Envirotech operates as an innovative leader within India's water conservation sector as it differs from other organizations that pursue profit-based solutions. Yooil exists beyond its entrepreneurial capacity since it functions as a reformist organization dedicated to transforming resource management practices.
Yooil Envirotech launched rubber dam technology into the market, which allowed them to execute projects that led to the recovery of complete agricultural areas. Their professional expertise leads to rubber dam construction that meets particular regional needs, thus achieving optimal water storage and delivery.
The Longest Rubber Dam in India represents Yooil’s advanced initiative, which brings revolutionary water storage solutions and flood protection mechanisms to the region. This project is a testament to their commitment to innovation and sustainability.
The company dedicates itself to establishing lasting environmental impact together with social benefits beyond its technological advancements. Rubber dams gain promotion from their team through their sustained adoption.
The increasing water conservation needs can be solved by the rubber dam in India, which presents new opportunities for sustainable agricultural water management. Yooil Envirotech takes an unyielding stand toward water conservation, which establishes it as more than a conventional company but an innovative force in India's water conservation development.
The future of efficient water resource management in India will depend heavily on rubber dams and the groundbreaking achievements of Yooil Envirotech. Yooil’s visionary attitude allows them to construct dams, which become the foundation for sustainable development across Indian agricultural areas and local communities.