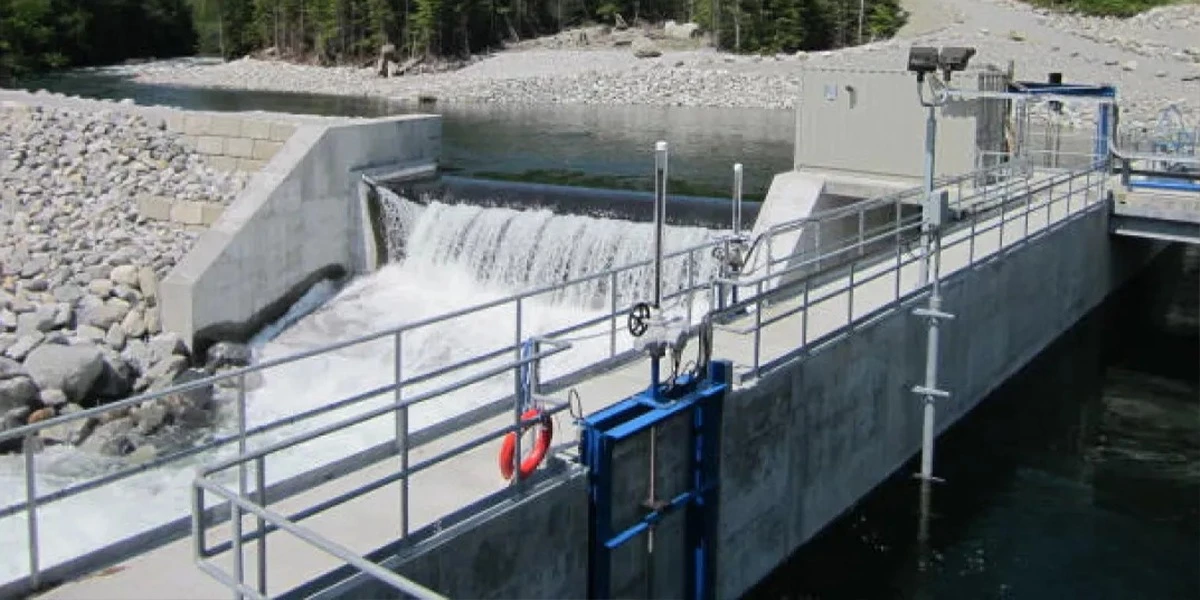
In the realm of water engineering, the future holds the promise of transformative innovations, and one technology that stands at the forefront of this evolution is the rubber dam. These flexible and versatile structures have been instrumental in addressing water management challenges across the globe. As we peer into the future, let's explore potential advancements in rubber dam technology, particularly in the context of India, a nation where water management plays a pivotal role in sustainable development.
Understanding Rubber Dams
Rubber dams, also known as inflatable rubber dams, are flexible barriers constructed from durable rubberized materials. They can be inflated with air to create temporary or permanent dams in water bodies. These dams have gained prominence as a versatile tool in various transforming water management applications, owing to their adaptability and eco-friendliness.
In India, where water management challenges are diverse and complex, it's imperative to rely on the expertise of top dam construction companies. Yooill Engineering, a name synonymous with excellence, is at the forefront of ushering in innovative advancements in rubber dam technology. With a legacy spanning over three decades and a portfolio boasting more than 400 successful projects worldwide, Yooill Engineering exemplifies a commitment to excellence in the field of water management.
In India, where water management is central to sustainable development, the future of water engineering holds immense promise. The potential advancements in rubber dam technology, driven by the expertise of companies like Yooill Engineering, are set to reshape the nation's approach to water management.
As India strives to achieve water security, optimize agricultural practices, and adapt to a changing climate, the synergy between technology and innovation in rubber dam technology will serve as a beacon of progress. It's a journey that promises a brighter, more water-secure future for India and its people.
In conclusion, the future of water engineering in India is a narrative of innovation, resilience, and sustainability. With rubber dams at the forefront of this transformation, India is poised to meet its water management challenges head-on and pave the way for a more prosperous and water-secure future.
1. What are rubber dams, and how do they work in water management?
Answer: Rubber dams are flexible barriers made of durable rubberized materials that can be inflated with air to control water flow. They work by creating temporary or permanent dams in water bodies, allowing precise control over water levels and flow.
2. How does advanced rubber dam technology contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Advanced rubber dam technology optimizes water distribution in agriculture. It ensures crops receive the right amount of irrigation, leading to increased yields, reduced water wastage, and improved sustainability.
3. What are the key advantages of using hybrid steel gate systems in rubber dams?
Answer: Hybrid steel gate systems combine the flexibility of rubber dams with the strength of steel gates. They offer enhanced durability and can withstand high water pressures, making them ideal for flood control and water storage in regions prone to heavy rainfall.
4. Can rubber dams be adapted to changing weather patterns caused by climate change?
Answer: Yes, rubber dams with advanced technology can adapt to changing weather patterns, including increased rainfall and prolonged droughts. Their flexibility and real-time control capabilities make them resilient against the impacts of climate change.
5. How do pocket dams work, and what are their applications in water management?
Answer: Pocket dams are small, portable dams that can be rapidly deployed to control and redirect water flow. They are used in emergency situations, such as flash floods, dam maintenance, and temporary water storage.
6. What role can bituminous geomembranes (BGM) play in water containment solutions?
Answer: Bituminous Geomembranes (BGM) are high-performance membranes made from bitumen. They offer exceptional resistance to water permeation and are used in water storage applications to prevent leakage and ensure efficient water containment.