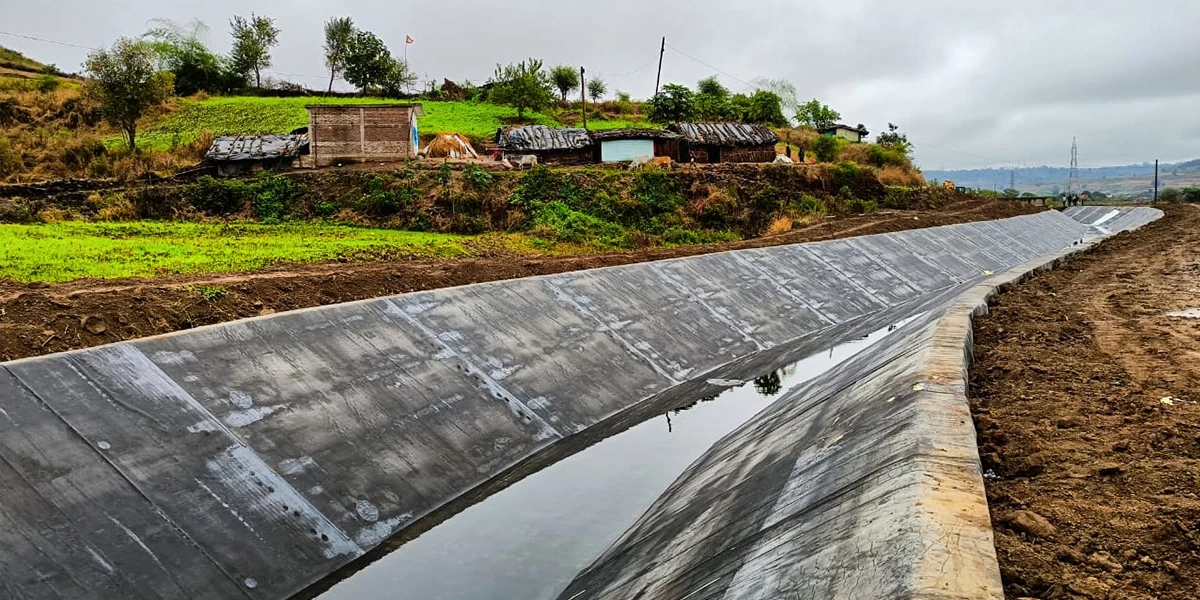
Canals, intricate lifelines that traverse landscapes, were instrumental in shaping civilisations and maintaining agriculture. Yet, the unchecked glide of water through these earthen channels often ends in seepage, evaporation, and waterlogging, diminishing their efficiency. To address those challenges, canal lining emerges as a capability solution. However, like any intervention in a complex atmosphere, it contains its own set of implications. This exploration delves into the multifaceted environmental impacts of canal lining, inspecting both its blessings and drawbacks.
Water scarcity looms massively as a global undertaking, necessitating modern solutions to optimise water aid control. Canal lining, which involves creating an impermeable layer in the canal mattress and banks, presents itself as a viable approach. By decreasing water losses through seepage and evaporation, canal lining targets enhancing water transport efficiency in agricultural fields.
Canal lining acts as a bulwark in opposition to water losses, notably lowering seepage and evaporation. This translates to a tremendous growth in the quantity of water reaching the fields, improving agricultural productivity and ensuring food security, particularly in regions grappling with water scarcity.
With an extra-controlled water flow, canal lining allows the adoption of contemporary irrigation strategies, together with drip and sprinkler systems. This minimises water wastage and maximises crop yields, optimising resource utilisation.
By stopping waterlogging and salinity, canal lining allows for the preservation of agricultural land. This, in turn, contributes to the general fitness of the atmosphere and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
Increased agricultural output, coupled with reduced water wastage, leads to stepped-forward economic conditions for farmers and the vicinity as a whole. Canal lining can contribute to poverty comfort and rural improvement by enhancing agricultural livelihoods.
While canal lining offers several balancing benefits, it's critical to remember its potential environmental impacts from a nuanced and comprehensive angle.
The construction of coated canals can disrupt herbal habitats, leading to a lack of biodiversity and atmospheric offerings. The alteration of water waft patterns can affect aquatic life, riparian flora, and the general ecological stability of the place.
The smooth, impermeable floor of lined canals can accelerate sedimentation in downstream regions, altering riverbeds and wetlands. This can impact water drift, erosion, and the general quality of water bodies with a great canal lining design. Additionally, canal lining can contribute to accelerated salinity in coastal areas by decreasing the dilution effect of freshwater influx.
While canal lining can enhance agricultural productivity, its blessings may not be evenly disbursed. Small-scale farmers and marginalised groups may additionally face demanding situations in having access to and utilising the improved water sources. Furthermore, the initial investment and renovation charges related to canal lining can be sizeable, probably affecting the affordability and accessibility of this generation for positive groups.
The pumping of water through lined canals can increase strength intake, especially in regions with restricted energy infrastructure. This can make a contribution to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
Canal lining can affect the microbial ecology of the water, doubtlessly affecting the pleasantness of the pleasantness of the water and the fitness of aquatic organisms.
To maximise the benefits of canal lining while minimising its detrimental outcomes, a holistic and integrated technique is important. This includes careful planning, environmental impact checks, and the adoption of sustainable practices.
Conduct thorough assessments to assess the suitability of canal lining in every particular context, thinking about elements like soil kind, topography, ecological sensitivity, and socioeconomic conditions.
Implement measures to offset the ecological impacts of canal lining, consisting of developing artificial wetlands, fish passages, or riparian buffer zones.
Involve nearby communities in the choice-making method and make certain they benefit from the assignment.
Explore the usage of eco-friendly and locally sourced materials for canal lining whenever feasible.
Establish a robust maintenance plan to prevent cracks, leaks, and sedimentation, ensuring the long-term performance and environmental integrity of the canal device.
Consider alternative water control strategies, inclusive of rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and efficient irrigation technologies, to complement canal lining and beautify standard water useful resource management.
Canal-lining initiatives ought to be aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to water and sanitation, food protection, and sustainable ecosystems. By integrating these dreams into undertaking planning and implementation, it is viable to gain both environmental and social benefits.
YOOIL Envirotech, a main provider of environmental solutions, acknowledges the complexities of water resource management. We offer a comprehensive range of services, including the fulfilled purpose of canal lining, to help groups optimise water utilisation while minimising environmental impacts. Our method combines current technology, sustainable materials, and expert engineering to deliver tailored answers that meet the particular wishes of every undertaking. We prioritise environmental stewardship and work intently with stakeholders to ensure that our tasks create a high-quality impact on the community and the atmosphere.
Addressing the challenges of water scarcity calls for a collaborative effort related to governments, groups, and personal zone organizations. By adopting sustainable practices like canal lining, applied with cautious consideration and mitigation measures, we will secure a water-stable destiny for generations to come. YOOIL Envirotech is dedicated to being part of this global effort. We believe that through innovation, partnership, and a shared imagination and prescience, we will construct a more resilient and water-stable global. Contact YOOIL Envirotech now.